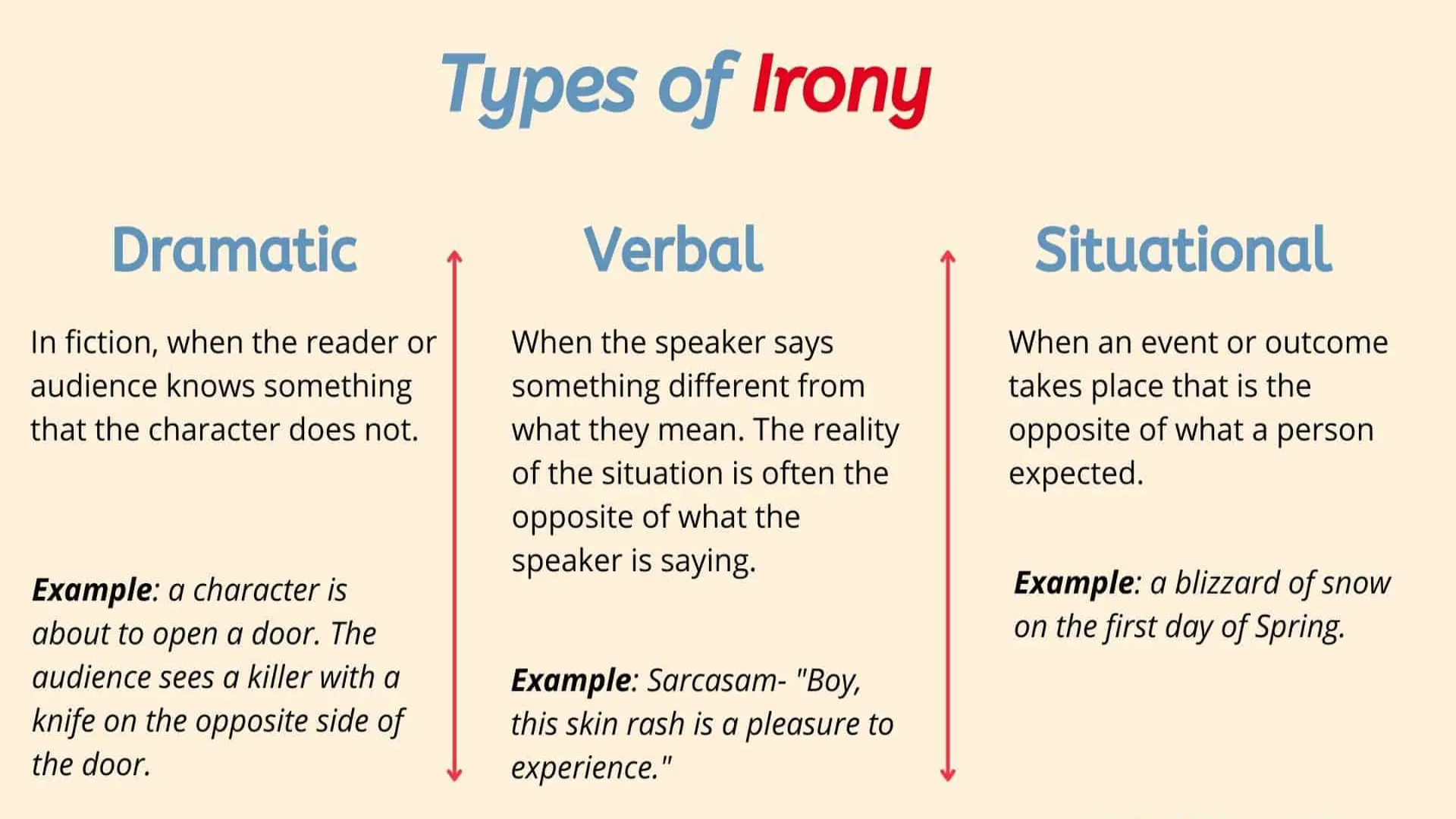
Irony is a literary device used to convey a meaning that is opposite or unexpected compared to the literal meaning. It is widely used in both literature and daily communication to add depth, humor, or complexity to statements. There are three main types of irony: verbal irony, situational irony, and dramatic irony. Let’s take a closer look at each of these to understand their unique qualities.
1. Verbal Irony
Verbal irony occurs when a speaker says something but means the opposite. It’s often used to express sarcasm, humor, or to emphasize a point. For instance, if it’s raining heavily and someone says, “What a beautiful day,” they are using verbal irony. The contrast between what is said and what is meant creates a clear irony in the situation.
2. Situational Irony
Situational irony happens when there is a discrepancy between what is expected to happen and what actually happens. For example, imagine a fire station burning down. The expectation is that a fire station should be safe from fires, but the actual event contradicts that expectation. This type of irony is often used to surprise the audience and highlight contradictions.
3. Dramatic Irony
Dramatic irony occurs when the audience knows something that the characters in the story do not. This type of irony creates suspense or humor. A common example is in horror movies where viewers know the killer is lurking, but the characters remain unaware. This creates tension as the audience waits for the characters to discover the truth.<-top:0em; margin-bottom:1em;">
